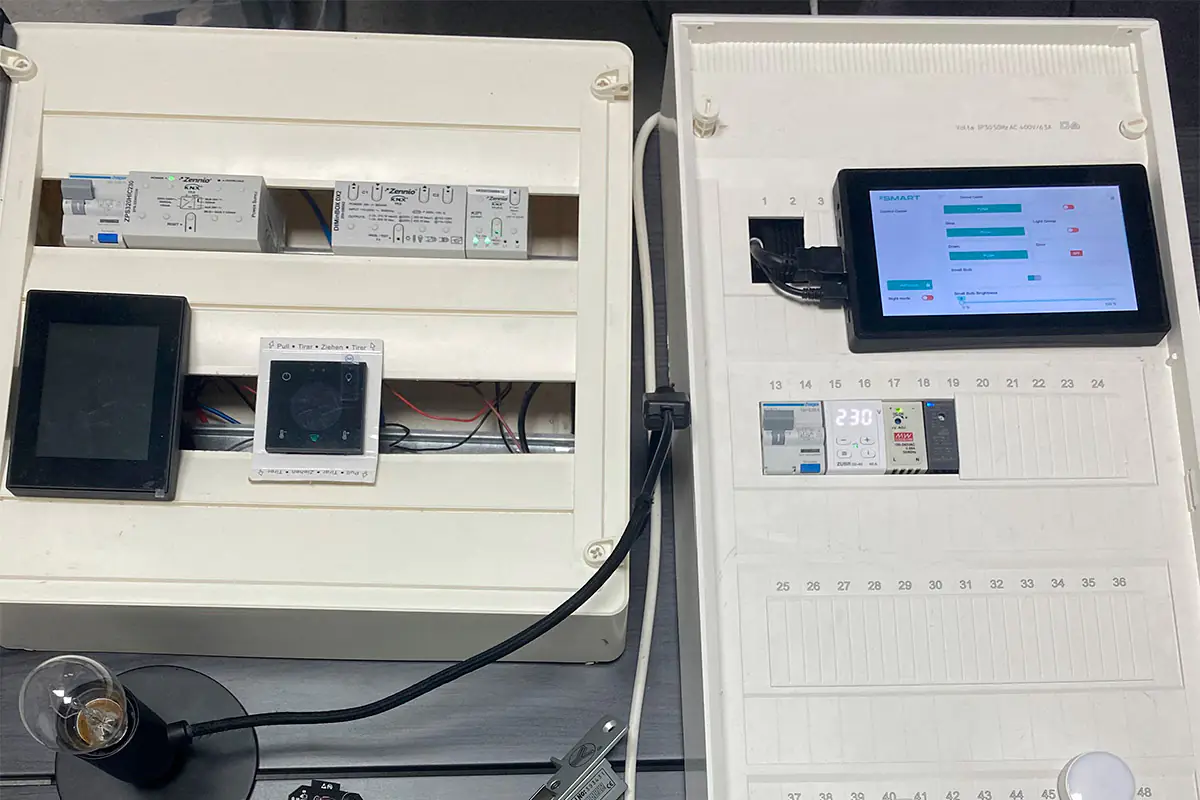
The Future of Smart Farming Using IoT [Webbylab`s Experience]
Written by:

Kostiantyn Oliynyk
Head of IoT at Webbylab
With a robust academic background in Telecommunication Systems Engineering, I apply my knowledge to lead innovations in the IoT domain. Starting as the first team member in the newly formed IoT department at WebbyLab, I've spearheaded its growth, fostering the expansion into embedded and hardware development alongside our core software projects. My dedication lies in pushing the boundaries of IoT technology, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence that profoundly impacts our clients' operational success.
Nanotechnology involves using nanoparticles, nano-encapsulated fertilizers, and pesticides that enable the gradual release of nutrients and chemicals. It allows for increased efficiency of fertilizer use.
There are numerous use cases of IoT in precision agriculture. The most prominent include crop monitoring, cattle management, weather monitoring, field mapping, greenhouse automation, precision steering, and semi-automated driving.
IoT allows for real-time farming data collection and transfer for further analysis by farmers. This tech helps improve agriculture monitoring and optimize resources. It also provides advanced insights into developing patterns and trends in fields and farms.
There are three components of precision agriculture: information, technology, and management. They correspond to the importance of data collection, advanced techs like IoT or machine learning models, and the efficient management of agricultural processes.
Geoinformatics and geographic information systems (GIS) allow for analyzing land, visualizing field data on maps, and studying them for further application in crop management.