Exploring Machine Learning Applications on Edge Devices
Written by:

Kostiantyn Oliynyk
Head of IoT at Webbylab
With a robust academic background in Telecommunication Systems Engineering, I apply my knowledge to lead innovations in the IoT domain. Starting as the first team member in the newly formed IoT department at WebbyLab, I've spearheaded its growth, fostering the expansion into embedded and hardware development alongside our core software projects. My dedication lies in pushing the boundaries of IoT technology, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence that profoundly impacts our clients' operational success.
FAQ
Can ML models run on low-power microcontrollers?
Yes. This field is known as TinyML, short for tiny machine learning. It involves using highly compressed ML models optimized for smaller, less powerful devices. Powered by lightweight architectures such as 1D CNNs, RNNs, or FNNs, these solutions can run efficiently on low-power microcontrollers, including ESP32 and STM32.
How does edge AI compare to cloud ML in latency and privacy?
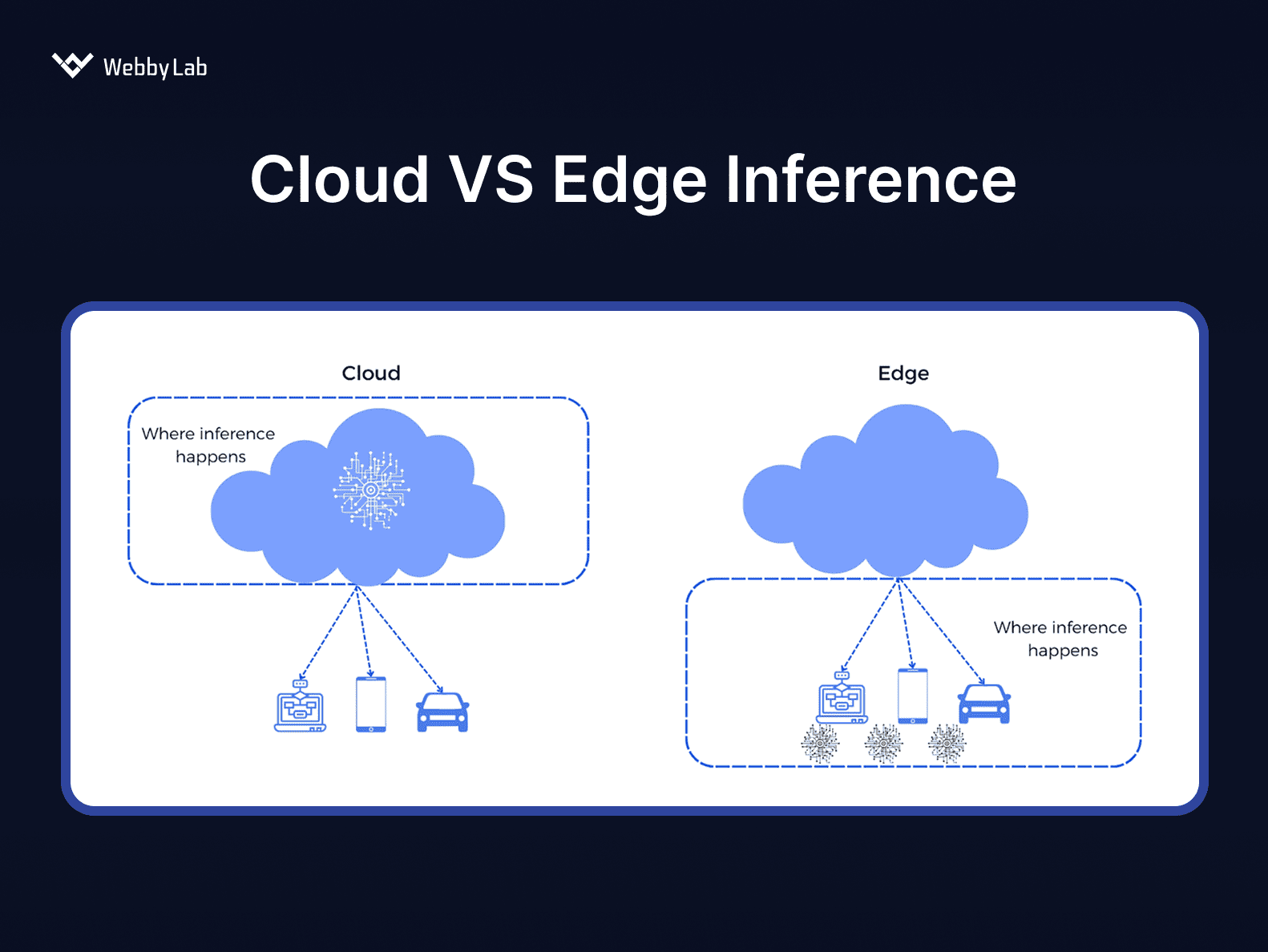
Edge cloud orchestration debate lies in the fact that edge AI enables faster response times because inference happens locally and improves privacy since raw data stays on-device.
Which types of applications benefit most from edge AI?
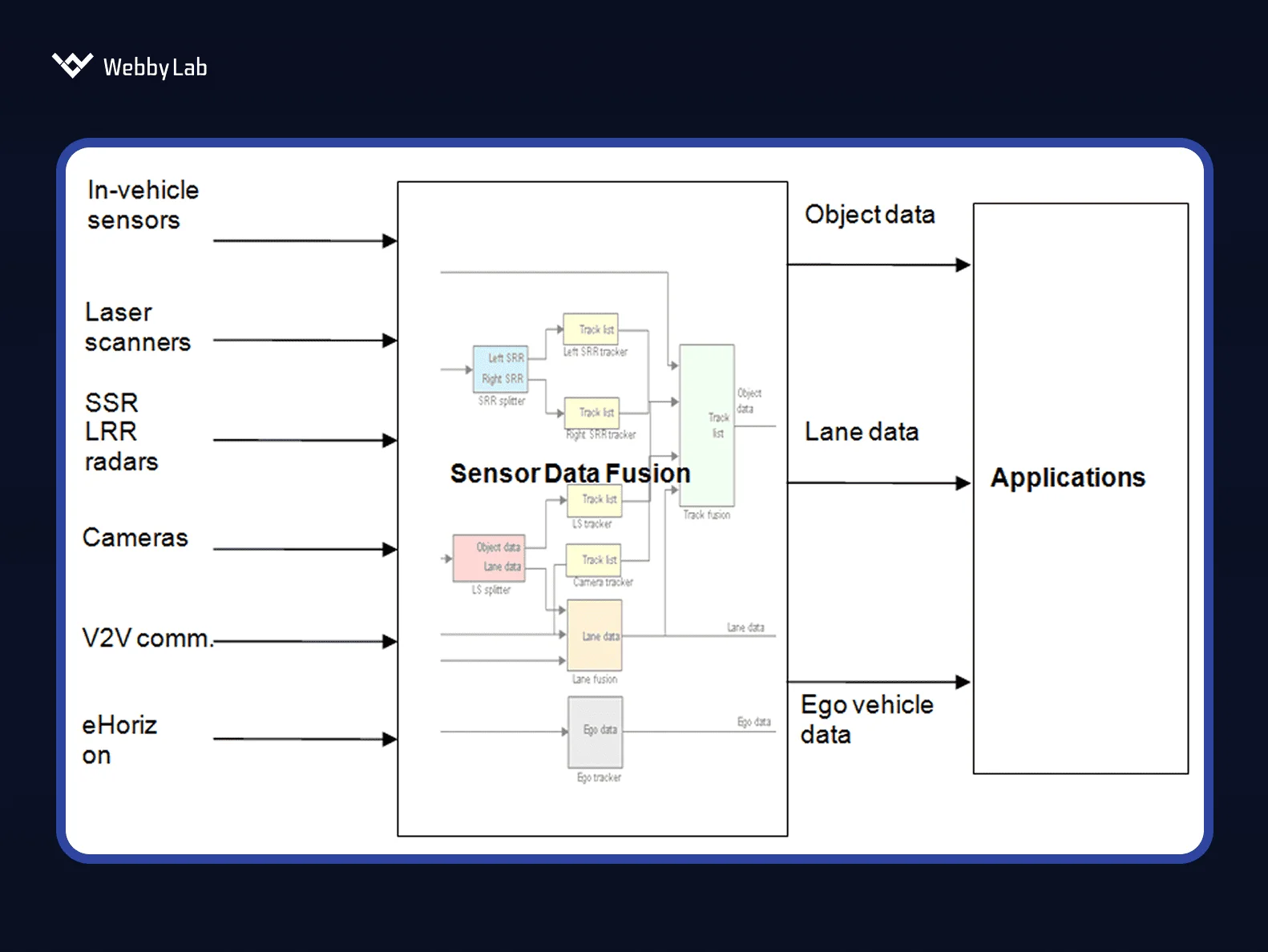
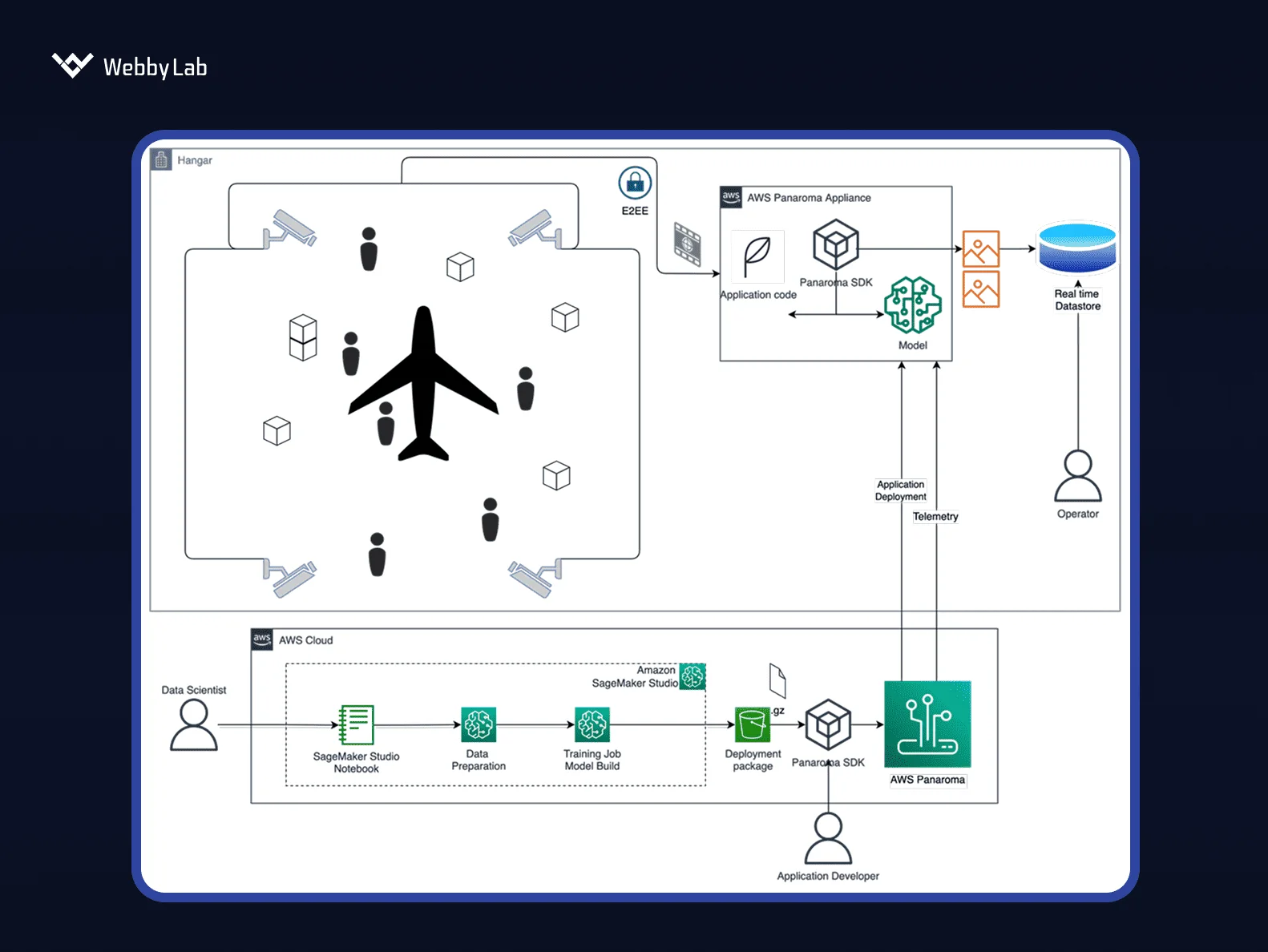
Real-time, offline, or privacy-sensitive workloads, such as predictive maintenance, audio event detection, safety monitoring, energy optimization, and on-device vision, benefit most.
What open-source tools help deploy ML on edge devices?
On-device machine learning for IoT sensors can be deployed through TensorFlow Lite Micro, ESP-DL ML library, OpenCV, AI-on-the-edge-device, and ESP32 LLM.
How do enterprises manage updates and OTA deployments for edge models?
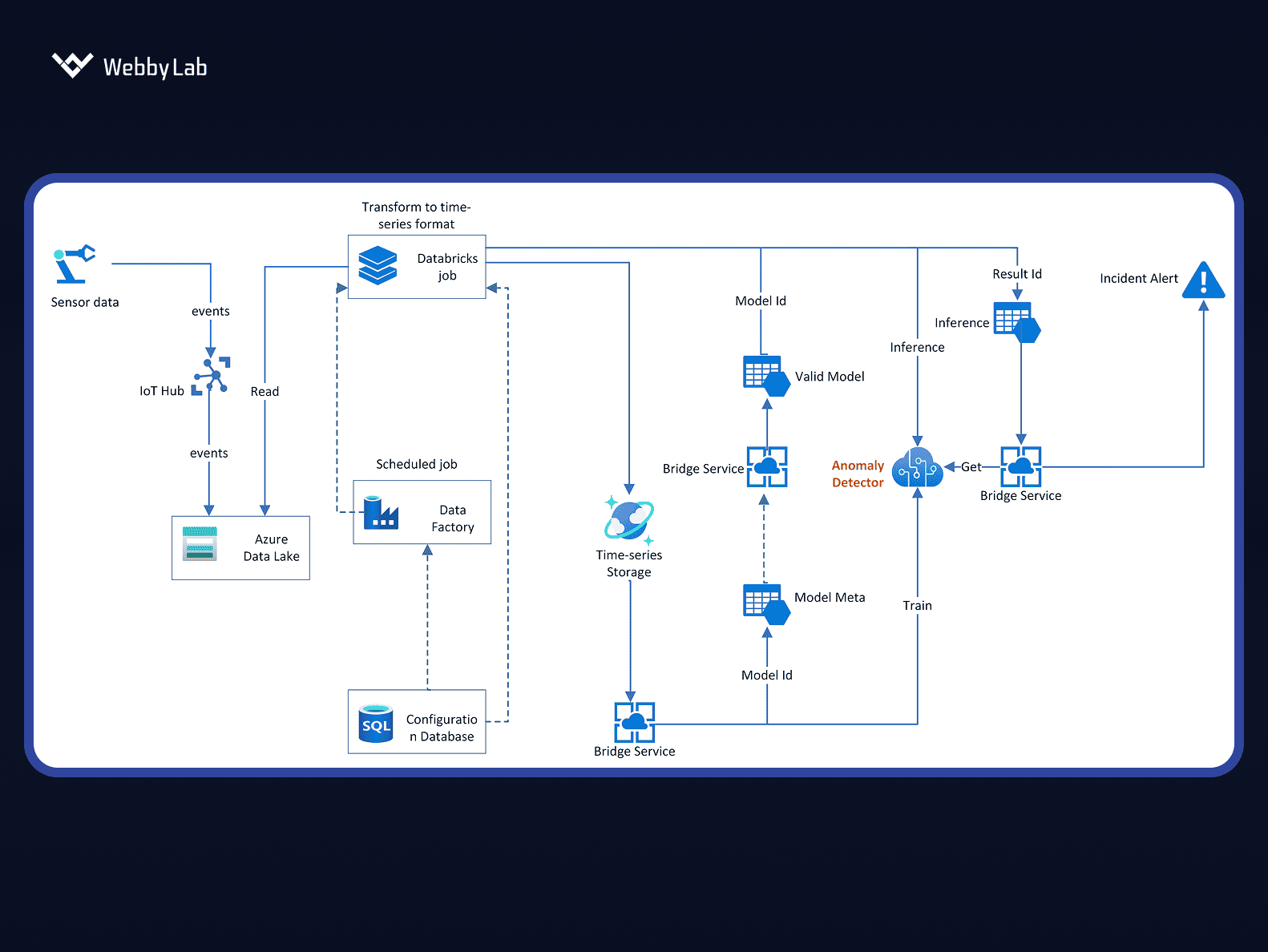
Most use centralized orchestration platforms with secure OTA updates, versioning, and staged rollout policies. These tools allow them to deploy, monitor, and fine-tune models across distributed fleets of devices without physical access.