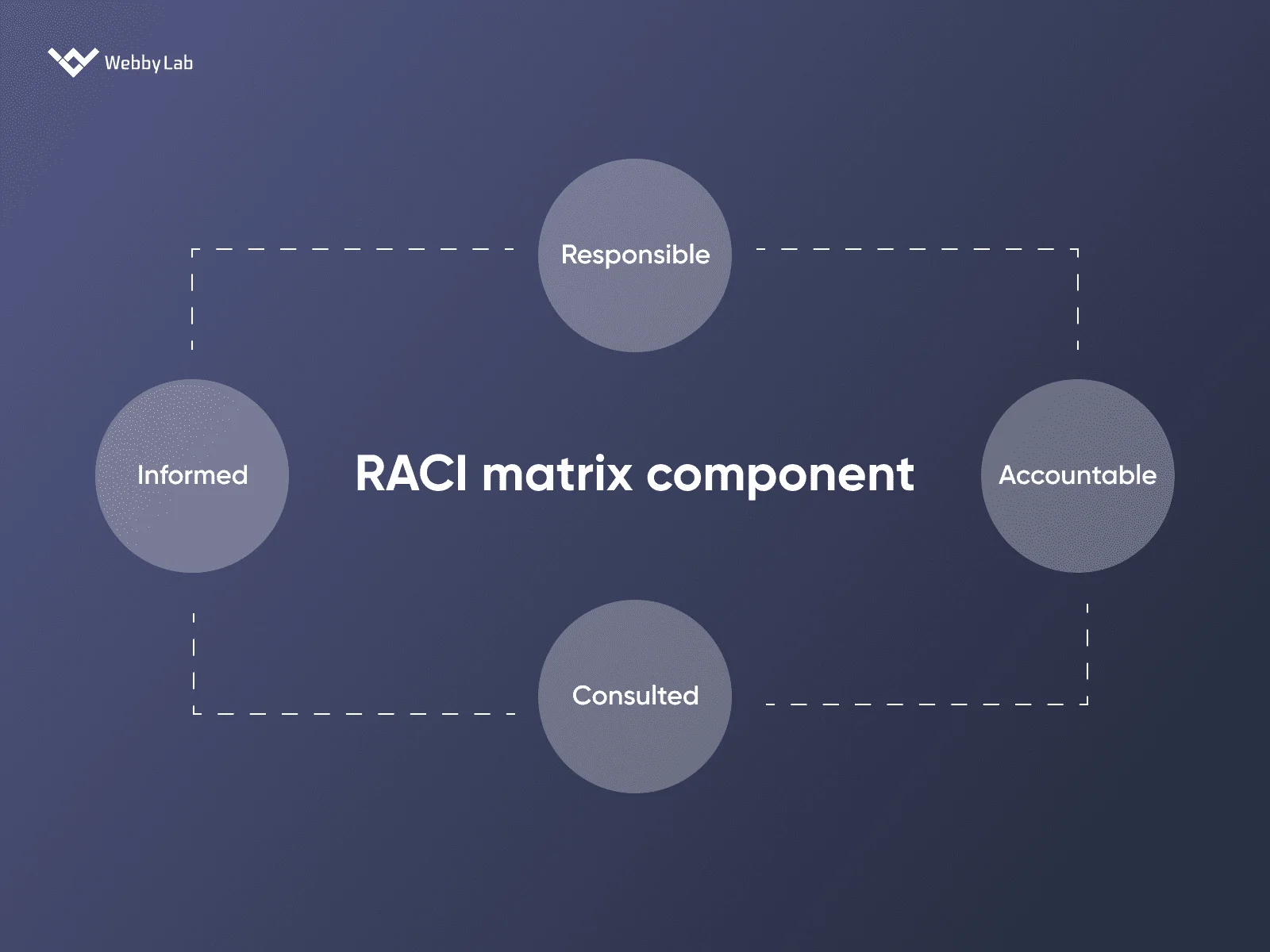
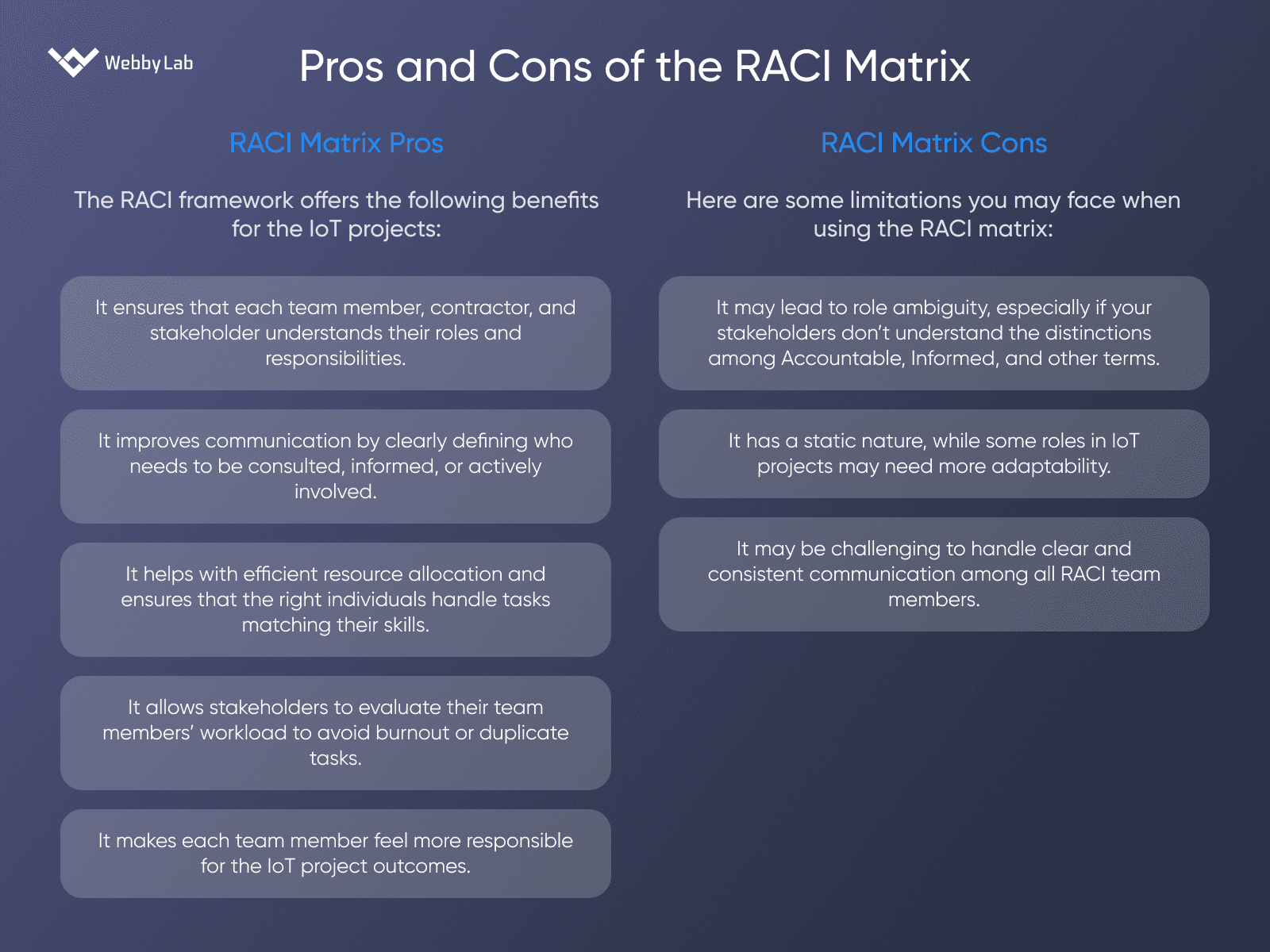
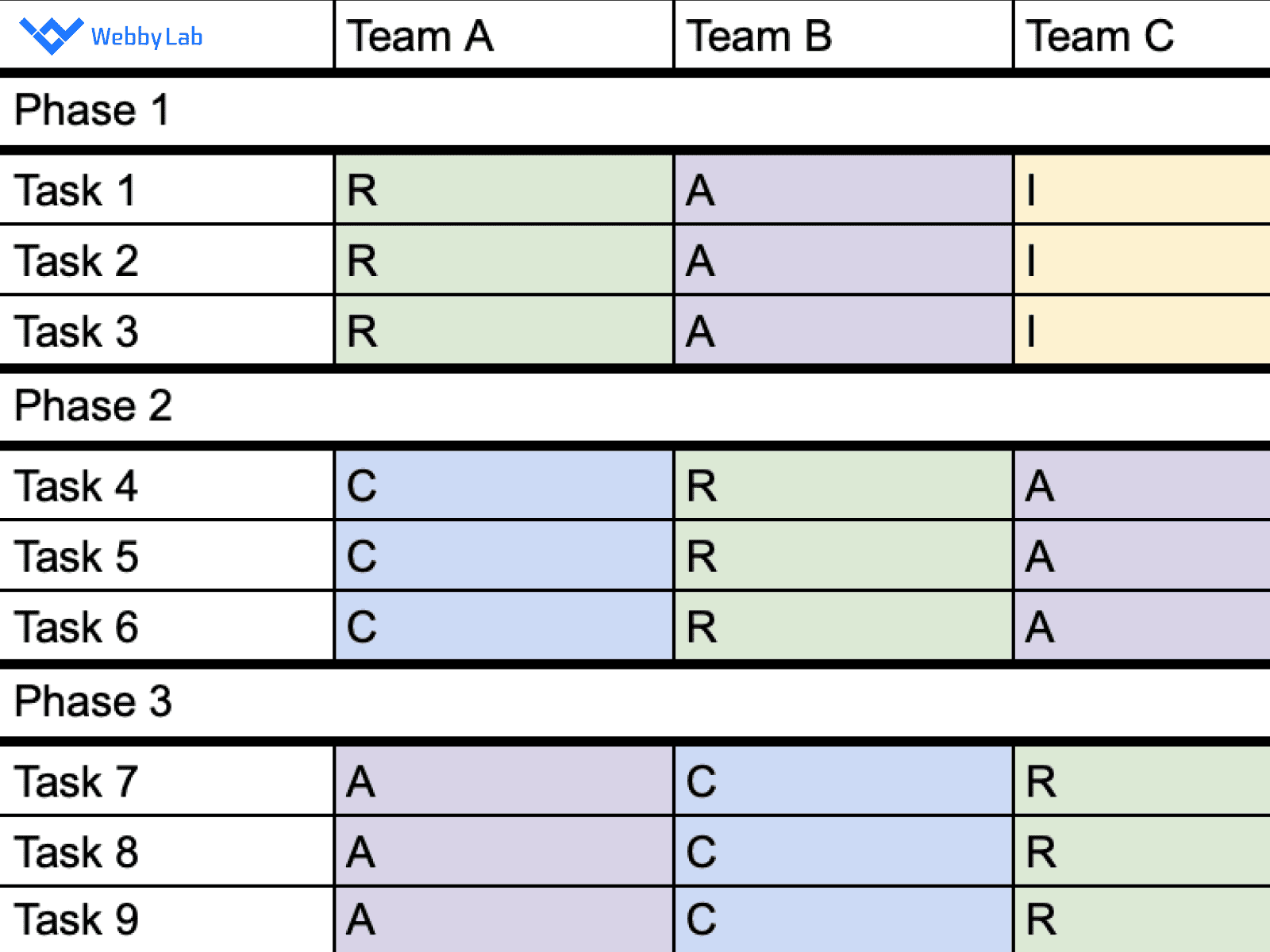
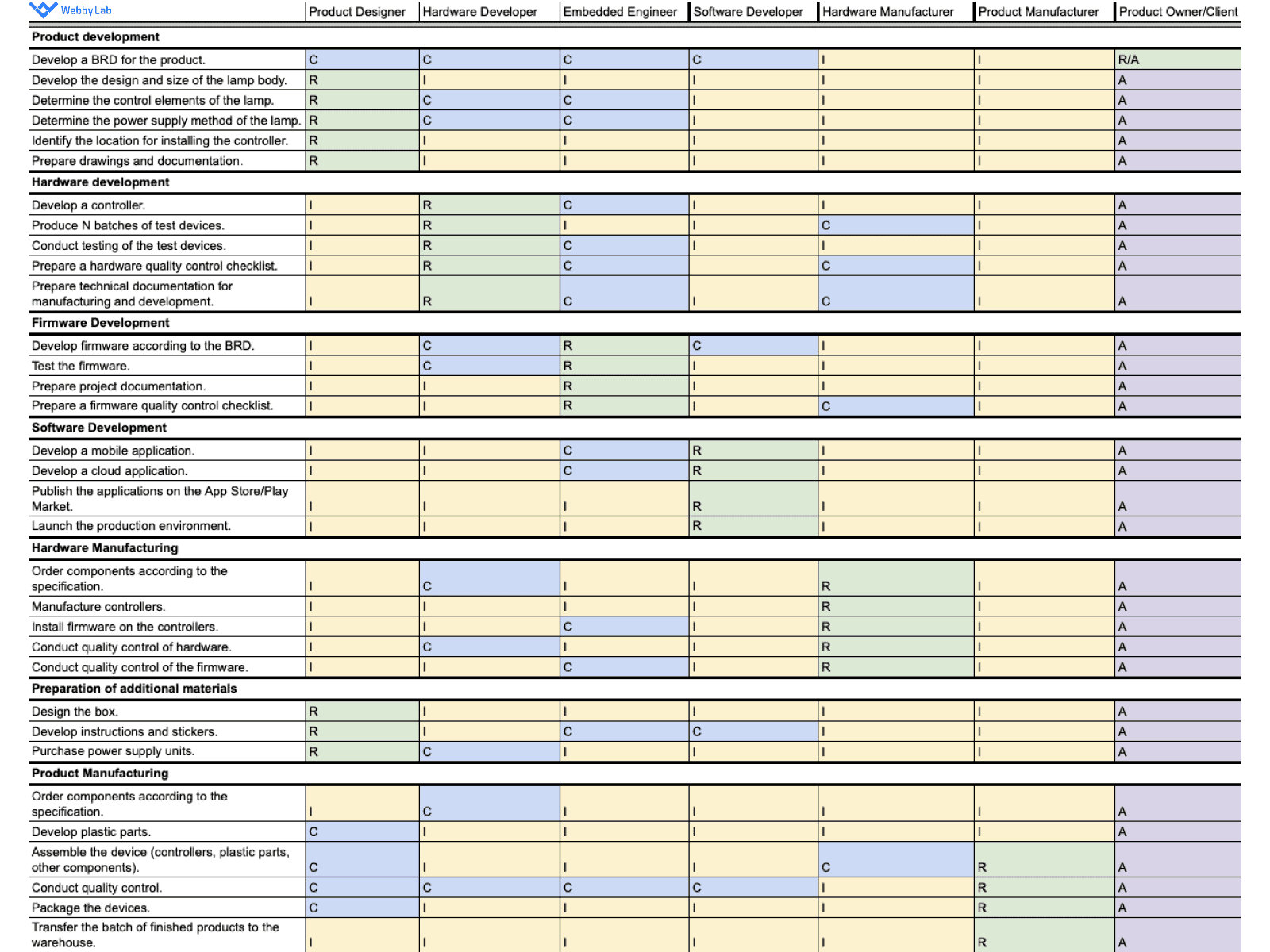
Optimizing IoT Project Management with RACI Matrix
Written by:

Kostiantyn Oliynyk
Head of IoT at Webbylab
With a robust academic background in Telecommunication Systems Engineering, I apply my knowledge to lead innovations in the IoT domain. Starting as the first team member in the newly formed IoT department at WebbyLab, I've spearheaded its growth, fostering the expansion into embedded and hardware development alongside our core software projects. My dedication lies in pushing the boundaries of IoT technology, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence that profoundly impacts our clients' operational success.
You may also like