Protecting Your IoT Infrastructure: Essential MQTT Security Practices
Written by:

Kostiantyn Oliynyk
Head of IoT at Webbylab
With a robust academic background in Telecommunication Systems Engineering, I apply my knowledge to lead innovations in the IoT domain. Starting as the first team member in the newly formed IoT department at WebbyLab, I've spearheaded its growth, fostering the expansion into embedded and hardware development alongside our core software projects. My dedication lies in pushing the boundaries of IoT technology, fostering a culture of innovation and excellence that profoundly impacts our clients' operational success.
FAQ
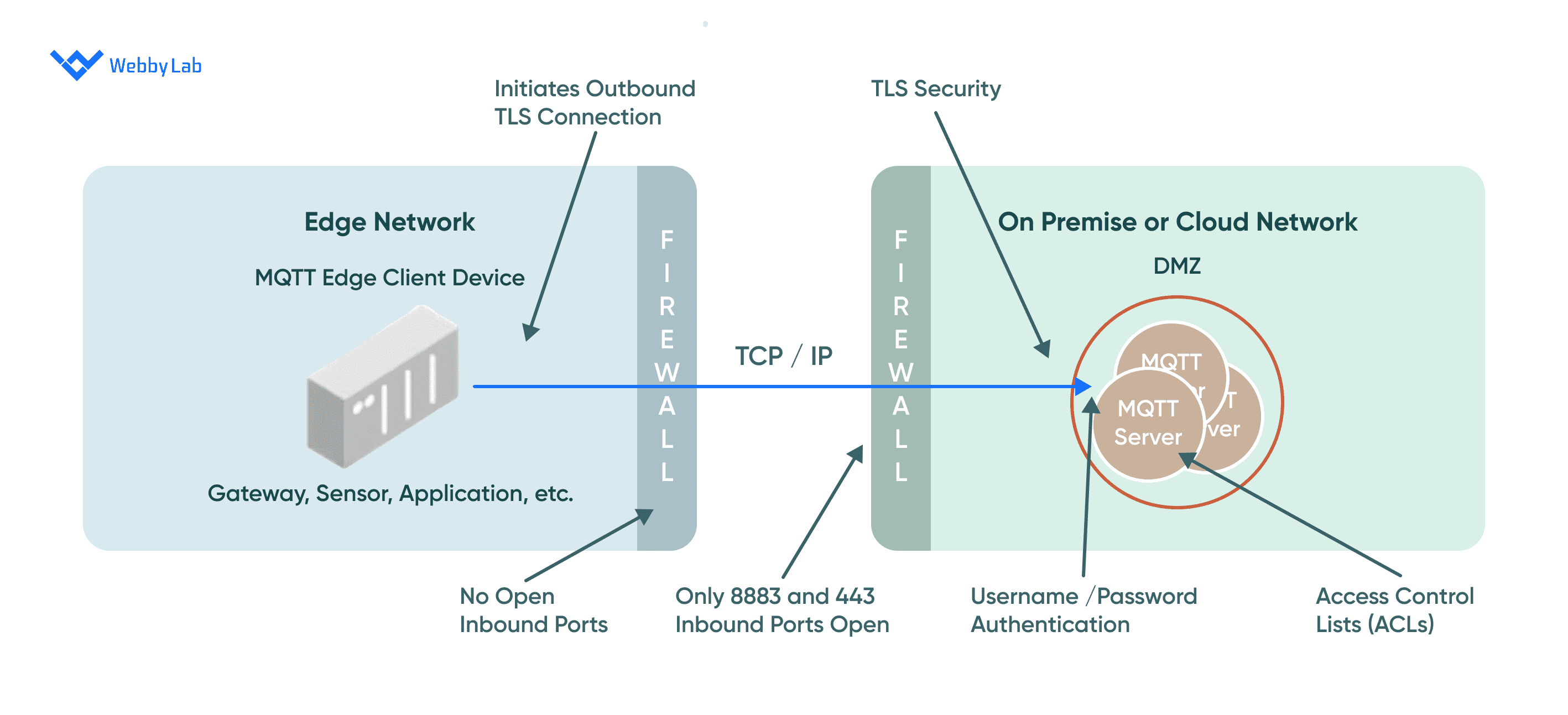
How do I make MQTT-based IoT devices secure?
To secure MQTT-based IoT devices, you should implement several fundamental principles, including application-layer authentication, encryption, and authorization. It’s also crucial to regularly update firmware and software to address security vulnerabilities and ensure continued protection.
What are the security essentials of MQTT?
The MQTT security essentials you should consider include the following:
Using strong usernames and passwords
Setting up access control lists to restrict device access
Using strict access permissions
Avoiding the use of wildcards in topic names
Using unique client IDs
Setting up secure bridges for remote connections
What are the key IoT security vulnerabilities?
When deploying your IoT system, you can encounter the following vulnerabilities:
Weak authentication mechanisms
Poor encryption
Insufficient access controls
Poorly configured devices
Lack of security updates
These vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security risks. That’s why it’s critical to implement proper security measures and best practices in IoT deployments.
What are some common security threats associated with MQTT-based IoT devices?
You can encounter the following types of security threats that affect MQTT-based IoT devices:
Unauthorized access
Data breaches
Message tampering or interception
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks
The above threats can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the IoT system and its data.
How can I test the security of my IoT system?
You can use specific tools to test your IoT system’s security. These include MQTT.fx, MQTTFx, and MQTT Inspector, which help monitor network traffic and test the encryption and authentication protocols. Security testing for web applications ensures that IoT systems are protected against vulnerabilities, safeguarding sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. You can also conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify potential security weaknesses.