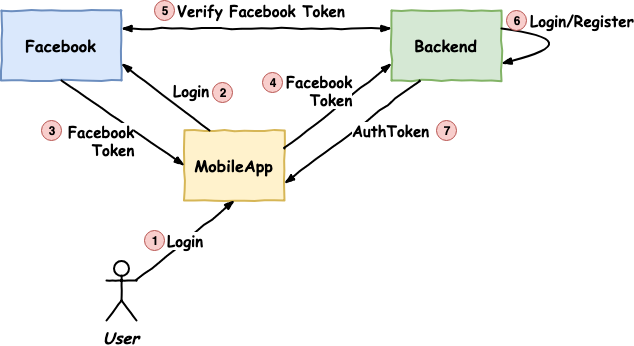
Facebook Login in React Native: How to Connect It in 3 Easy Steps
As described in [Login example](https://github.com/thebergamo/react-native-fbsdk-next#login) in `react-native-fbsdk-next` you can use the first argument of `onLoginFinished` callback, which will contain an error if such occurred.
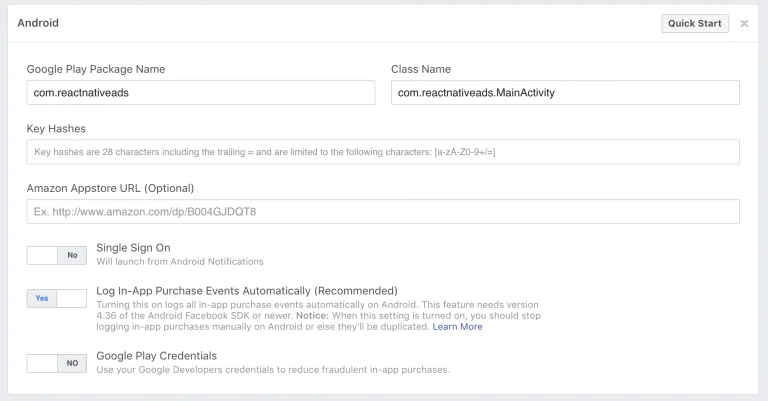
Despite the fact that in most cases it is more difficult to integrate with iOS, here more difficulties appear with Android. All because of non-obvious key hashes that must be generated and registered.
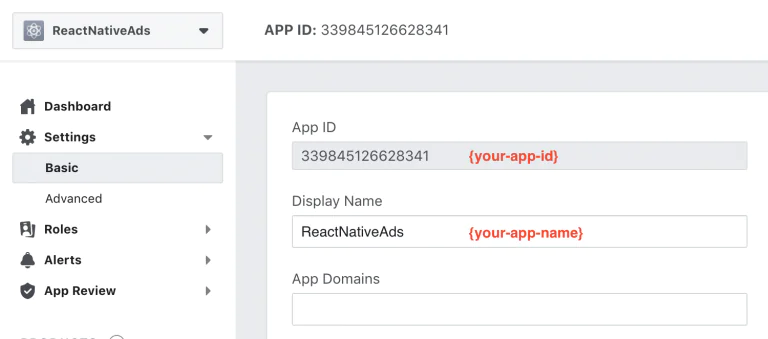
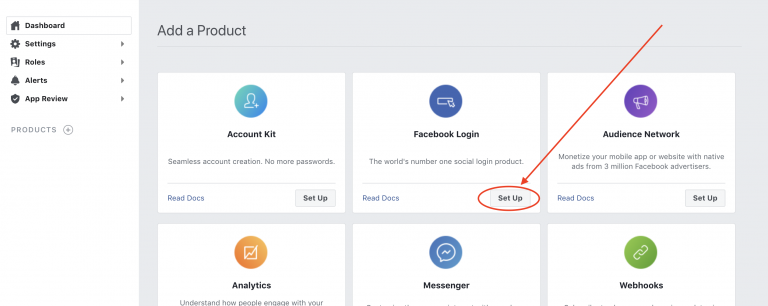
You can switch `App mode` in Facebook (Meta) developer’s [dashboard](https://developers.facebook.com/apps/).
If we talk about Facebook Auth integration only, it will take about 2 days. If include to the estimate session management and backend integration – it’ll be about 5 days.








![Testing React Components with Hooks & Mocks [Full Guide]](https://webbylab.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/v3-768x260-1-768x260.png)



